Abstract
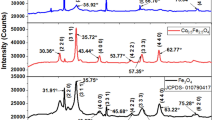
The effect of hydrogen reduction temperature on the properties of Fe–Ni powders was described. The mixed powders of Fe-oxide and NiO were prepared by chemical solution mixing of nitrates powders and calcination at 350 °C for 2 h in air. The calcined powders formed small agglomeration with an average particle size of 100 nm. The microstructure and magnetic properties were investigated by using X-ray diffractometry, thermogravimetry, differential thermal analyzer, and vibrating sample magnetometer. Microstructure and thermal analysis revealed that the Fe-oxide and NiO phase were changed to FeNi3 phase in the temperature range of 245–310 °C, and by heat-up to 690 °C the FeNi3 phase was transformed to γ-FeNi phase. The reduced powder at 350 °C showed saturation magnetization of 76.3 emu/g and coercivity of 205.5 Oe, while the reduced powders at 690 °C exhibited saturation magnetization of 84.0 emu/g and coercivity of 14.0 Oe. The change of magnetic properties was discussed by the observed microstructural features.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.L. Wallace, IEEE Trans. Magn. 29, 4209 (1993)
K.J. Vinoy, R.M. Jha, Radar Absorbing Materials from Theory to Design and Characterization (Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston, 1996), p. 13
Y. Nie, H.H. He, R.Z. Gong, X.C. Zhang, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 310, 13 (2007)
X. Lu, G. Liang, Y. Zhang, Mater. Sci. Eng. B139, 124 (2007)
B.-H. Lee, Y.J. Lee, K.H. Min, D.-G. Kim, Y.D. Kim, Mater. Lett. 59, 3156 (2005)
C. Duhamel, Y. Champion, M. Trencé, M. Walls, J. Alloy Compd. 393, 204 (2005)
Z.H. Wang, C.J. Choi, J.C. Kim, B.K. Kim, Z.D. Zhang, Mater. Lett. 57, 3560 (2003)
M. Tomonari, K. Ida, H. Imanishi, T. Yonezawa, K. Mori, H. Yamashita, Res. Chem. Intermed. 34, 641 (2008)
S.-T. Oh, M.-H. Joo, Y.-H. Choa, K.H. Kim, S.-K. Lee, Phys. Scr. T139, 014050 (2010)
J.S. Lee, T.H. Kim, J.H. Yu, S.W. Chung, Nanostr. Mater. 9, 153 (1997)
S.F. Moustafa, W.M. Daoush, J. Mater. Proc. Tech. 181, 59 (2007)
T.B. Massalski, Binary Alloy Phase Diagram (American Society for Metals, Ohio, 1986), p. 267
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a grant from the Fundamental R&D Program for Core Technology of Materials funded by the Ministry of Knowledge Economy, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oh, ST., Choa, YH., Kim, K.H. et al. Effect of hydrogen reduction temperature on the microstructure and magnetic properties of Fe–Ni powders. Res Chem Intermed 36, 851–857 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-010-0192-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-010-0192-8